Cables 101

CIRCUIT SYMBOLS 101 | CONNECTORS 101 | CABLES 101 | LAMPS 101 | LEDS 101 | RELAYS 101 | SWITCHES 101
Cable... flex... lead... wire... what do all these terms mean?
-
A cable is an assembly of one or more conductors (wires) with some flexibility.
-
A flex is the proper name for the flexible cable fitted to mains electrical appliances.
-
A lead is a complete assembly of cable and connectors.
-
A wire is a single conductor which may have an outer layer of insulation (usually plastic).
![]()
Single core equipment wire
This is one solid wire with a plastic coating available in a wide variety of colours. It can be bent to shape but will break if repeatedly flexed. Use it for connections which will not be disturbed, for example links between points of a circuit board.
Typical specification: 1/0.6mm (1 strand of 0.6mm diameter), maximum current 1.8A.
Stranded wire
This consists of many fine strands of wire covered by an outer plastic coating. It is flexible and can withstand repeated bending without breaking. Use it for connections which may be disturbed, for example wires outside cases to sensors and switches. A very flexible version ('extra-flex') is used for test leads.
Typical specifications:
10/0.1mm (10 strands of 0.1mm diameter), maximum current 0.5A.
7/0.2mm (7 strands of 0.2mm diameter), maximum current 1.4A.
16/0.2mm (16 strands of 0.2mm diameter), maximum current 3A.
24/0.2mm (24 strands of 0.2mm diameter), maximum current 4.5A.
55/0.1mm (55 strands of 0.1mm diameter), maximum current 6A, used for test leads.
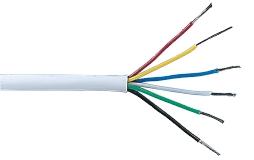
Signal cable
Signal cable consists of several colour-coded cores of stranded wire housed within an outer plastic sheath. With a typical maximum current of 1A per core it is suitable for low voltage, low current signals where screening from electrical interference is not required. The picture shows 6-core cable, but 4-core and 8-core are also readily available.
|
Screened cable (mono) |
 |
|
Screened cable (stereo) |
 |
|
Screened cable (stereo) |
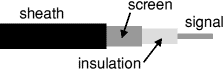
Screened cable
The diagram shows the construction of screened cable. The central wire carries the signal and the screen is connected to 0V (common) to shield the signal from electrical interference. Screened cable is used for audio signals and dual versions are available for stereo.
 |
|
|
Construction of a screened cable |
Co-axial cable
This type of screened cable (see above) is designed to carry high frequency signals such as those found in TV aerials and oscilloscope leads.
Mains flex
|
|
Flex is the proper name for the flexible cable used to connect appliances to the mains supply. It contains 2 cores (for live and neutral) or 3 cores (for live, neutral and earth). Mains flex has thick insulation for the high voltage (230V in UK) and it is available with various current ratings: 3A, 6A and 13A are popular sizes in the UK. Mains flex is sometimes used for low voltage circuits which pass a high current, but please think carefully before using it in this way. The distinctive colours of mains flex should act as a warning of the mains high voltage which can be lethal; using mains flex for low voltage circuits can undermine this warning.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

